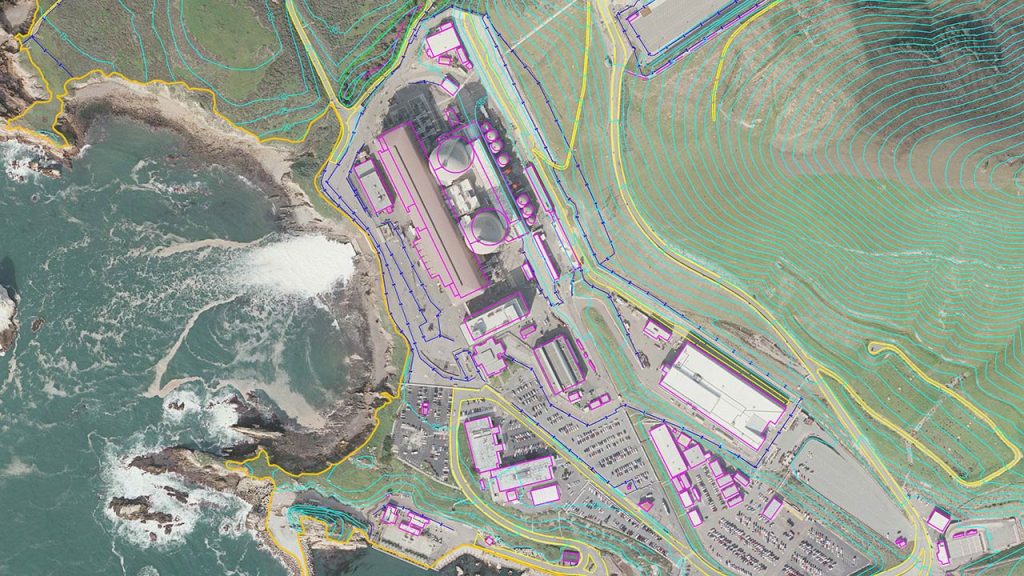
In the modern era of geography and environmental studies, understanding remote sensing in geospatial mapping has become essential for researchers, urban planners, and environmentalists alike. Remote sensing technology allows us to capture information about the Earth’s surface without direct physical contact, providing invaluable data for analysis, decision-making, and planning.
What is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing refers to the process of acquiring information about an object or area from a distance, typically using satellites, drones, or aerial sensors. This technology collects data in the form of images, spectra, or radar signals that can be interpreted to understand surface characteristics, vegetation, water bodies, and urban infrastructure.
The integration of remote sensing in geospatial mapping has revolutionized the way we study landscapes, monitor environmental changes, and manage natural resources. It allows for rapid and accurate data collection across large and often inaccessible areas.
Applications of Remote Sensing in Geospatial Mapping
Environmental Monitoring
One of the most significant uses of remote sensing in geospatial mapping is monitoring environmental changes. Satellite imagery can track deforestation, desertification, climate change impacts, and natural disasters. For instance, mapping flood-prone areas or monitoring ice melting in polar regions relies heavily on remote sensing data.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Urban planners use remote sensing data to assess land use, infrastructure development, and population growth patterns. This helps in designing sustainable cities, managing traffic systems, and planning for disaster management.
Agriculture and Forestry
Farmers and foresters benefit from remote sensing for crop monitoring, soil analysis, and forest management. Geospatial maps created using remote sensing data can indicate soil moisture levels, crop health, and forest cover changes over time.
Advantages of Remote Sensing in Geospatial Mapping
- Large Area Coverage: Remote sensing allows for mapping extensive areas quickly and efficiently.
- Cost-Effective: It reduces the need for physical surveys, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Accuracy and Precision: Advanced sensors capture detailed information, which enhances the reliability of geospatial maps.
- Timely Updates: Frequent satellite passes enable real-time monitoring of changes in landscapes and urban environments.
Future Trends
The future of understanding remote sensing in geospatial mapping is closely tied to advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-resolution satellite imagery. These technologies are improving the accuracy of spatial data interpretation and making predictive analysis more accessible.
Additionally, the use of drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is expanding, offering localized high-resolution imagery for various industries, from agriculture to disaster management.
Conclusion
Understanding remote sensing in geospatial mapping is critical for leveraging technology to analyze and manage the Earth’s surface efficiently. From environmental monitoring to urban planning, remote sensing provides a powerful toolkit for informed decision-making and sustainable development. As technology evolves, its role in geospatial mapping will continue to grow, offering even more precise and actionable insights.